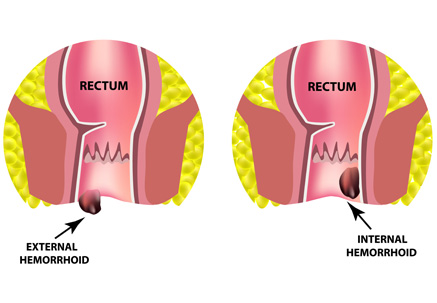
How are hemorrhoids diagnosed?
Your doctor typically makes a diagnosis by discussing your history of symptoms, particularly focusing on bowel habits. Your doctor will also use physical examination to confirm the diagnosis of hemorrhoids, including the use of anoscopy which can be used to rule out other potential problems like anal fissures, fistulas and rashes.
How are hemorrhoids treated?
Medical treatment
The most significant method of treating hemorrhoids is modifying stool through increased fiber in the diet, 25g/day for women and 38 g/day for men. You can also use stool softener’s (docusate) and lubricant laxatives(mineral oil) or bulking agents (psyllium) to help prevent constipation.
Toileting behavior
Avoid straining in the restroom and do not spend more than 3 to 5 minutes having a bowel movement. Avoid reading in the restroom.
Sitz bathes
Place warm water in a bathtub or portable device for 15 minutes at a time for pain relief.
Medications
Your doctor may offer you topical creams including steroids or local anesthetics to help with hemorrhoid flares. These creams don’t cure the problem but relieve the symptoms and should not be used for more than a month at a time without seeing your doctor.
Office Procedures
Rubber band ligation
This is the most common office procedure to treat internal hemorrhoids. Your doctor places a rubber band around the hemorrhoids to make them shrink and remove them. Typically this is done with only symptoms of pressure afterwards and dull ache but no severe pain.
Excision of thrombosed hemorrhoid
If you present to the doctor with signs of a thrombosed hemorrhoid that is very painful then this can be removed in the office under local anesthesia.
Operative procedures
If the hemorrhoids are significantly enlarged and it is necessary, your doctor will perform excisional hemorrhoidectomy. This is done as an outpatient surgery with you going home the same day.